Komtac|Dongcheng
Dongze|Huaisong


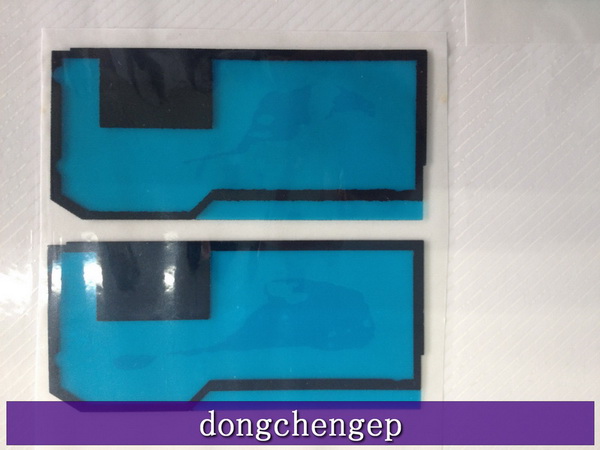
supply OEM Die-Cut electronic auxiliary material
Die-Cut electronic material
Raw material including PE foam ,XPE foam,3M adhesive tape, PE sheet or conduct material, composite material..
OEM various shape
The Importance of Die-Cutting in Electronic Auxiliary Components: Precision, Efficiency, and Innovation
Introduction
Die-cutting is a crucial manufacturing process widely used in the electronics industry, particularly in the production of electronic auxiliary components. These components, which include gaskets, insulators, EMI shields, and adhesive tapes, are essential for the proper functioning and longevity of electronic devices. This article explores the importance of die-cutting in the production of electronic auxiliary components, highlighting its benefits, applications, and the innovative advancements in this field.
Understanding Die-Cutting
Die-cutting is a fabrication process that involves cutting, shaping, and forming materials using a specialized tool called a die. This process can be used on a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, foams, and adhesives. In the context of electronic auxiliary components, die-cutting is used to produce precision parts that meet specific design and functional requirements.
1. Types of Die-Cutting:
- Flatbed Die-Cutting: Utilizes a flatbed press and is suitable for thicker materials and large production runs.
- Rotary Die-Cutting: Involves cylindrical dies and is ideal for high-speed and high-volume production.
- Laser Die-Cutting: Employs lasers to cut materials and is perfect for intricate designs and low to medium production volumes.
2. Materials Used:
- Foams: Used for cushioning and insulation.
- Adhesives: Used for bonding and sealing.
- Metals: Used for EMI/RFI shielding and grounding.
- Plastics:** Used for insulation and protective barriers.
Benefits of Die-Cutting in Electronic Auxiliary Components
1. Precision and Accuracy:
- Tight Tolerances: Die-cutting allows for the creation of components with very tight tolerances, ensuring precise fitting and functionality in electronic assemblies.
- Consistent Quality: The process provides consistent and repeatable results, crucial for maintaining quality across large production runs.
2. Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness:
- High-Speed Production: Rotary die-cutting, in particular, enables high-speed production, making it suitable for high-volume manufacturing.
- Reduced Waste: The ability to optimize material usage during die-cutting helps in reducing waste and lowering production costs.
3. Versatility and Flexibility:
-Complex Shapes: Die-cutting can produce complex shapes and intricate designs that are often required in electronic components.
- Wide Material Compatibility: The process can be applied to a wide range of materials, making it versatile for various applications.
4. Customization:
- Tailored Solutions: Die-cutting allows for the customization of components to meet specific design requirements and application needs.
- Prototype Development: It facilitates rapid prototyping, enabling quick iterations and adjustments in the design phase.
Applications in Electronic Auxiliary Components
1. Gaskets and Seals:
- Function: Provide sealing, cushioning, and insulation to protect electronic components from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and vibration.
- Materials: Typically made from foam, rubber, or silicone.
2. Insulators:
- Function: Prevent electrical shorts by providing insulation between different conductive parts.
- Materials: Often made from plastic or rubber.
3. EMI/RFI Shields:
- Function: Protect electronic devices from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), ensuring signal integrity.
- Materials: Commonly made from conductive metals or fabrics.
4. Adhesive Tapes:
- Function: Bond, mount, and seal components within electronic devices.
- Materials: Include various adhesive-backed materials, such as foam tapes, film tapes, and conductive tapes.
Innovations and Future Trends
1. Advanced Materials:
- Nanomaterials: The use of nanomaterials in die-cutting is emerging, offering enhanced properties such as improved conductivity, strength, and flexibility.
- **Biodegradable Materials:** As sustainability becomes a focus, biodegradable and eco-friendly materials are being developed for die-cut components.
2. Digital Die-Cutting:
- Precision and Customization: Digital die-cutting technologies, such as laser die-cutting, allow for greater precision and customization, enabling the production of complex and intricate designs.
- Rapid Prototyping: Digital methods facilitate rapid prototyping, reducing development times and accelerating time-to-market.
3. Automation and Integration:
- Smart Manufacturing: The integration of automation and smart manufacturing technologies into die-cutting processes enhances efficiency, reduces human error, and allows for real-time monitoring and adjustments.
- Robotics: The use of robotics in die-cutting processes can further increase production speeds and consistency in future
4. Multi-Functional Components:
- Integrated Solutions: Future die-cut components may combine multiple functions, such as combining EMI shielding with thermal management or integrating adhesive properties with insulation.
Conclusion
Die-cutting is a vital process in the production of electronic auxiliary components, offering precision, efficiency, and versatility. As technology advances, innovations in materials, digital die-cutting, and automation are set to further enhance the capabilities and applications of die-cut components in the electronics industry. By continuing to leverage these advancements, manufacturers can produce higher quality, more reliable, and cost-effective components that meet the ever-evolving demands of modern electronic devices.


Address:3FL,Blck A#,Huimei Industry Park,Luwu, Zengbu, Chashan, Dongguan, Guangdong, China
Post Code:523383
E-mail: gary@dongchengep.com
Tel:+86-769-81800502
Mobile:+86-13712658816
Mr Gary shaw